Table of Contents
Whenever we write a program or develop an application whether it’s a web-based or a mobile application, our main goal is to utilize our available resources in the most effective way which is optimization. If we talk about Django performance, it slows down the application due to framework flexibility and some overheads like traffic, server response time, and frontend technologies. So, let’s discuss some tips that can be used to optimize Django performance including the execution time, length of code, and allocated memory.
Django is one of the most valuable frameworks these days as it provides a variety of features. Its predefined modules and libraries make it even more robust. The Python performance is slightly slower than some other programming language programs due to its dynamic nature.
Django Performance Optimization Tips
The following tips can help optimize the Django application performance:
- Database Optimization
- Code Optimization
- Caching
- Concept of Laziness
- Using performance booster functions
- Latest software version
- Managing a large number of requests
Database Optimization
Database optimization includes the queries optimization. Let’s suppose you have to enter 5000 new records. Rather than querying the database iteratively for every record, you should insert all the records at once by using a single query. For example, you can use the bulk_create() query for inserting the data records at one time.
Creating posts in the standard way:
Post.objects.create(title="Esketchers") Post.objects.create(title="ALGORITHMS") Post.objects.create(title="DJANGO") Post.objects.create(title="PYTHON")
It is accessing the database four times.
But by using the bulk_create method, we can do the same thing at 1 time as,
Post.objects.bulk_create( [Post(title='Machine Learning'), Post(title='ALGORITHMS'), Post(title='DJANGO'), Post(title='PYTHON') ])
Django by default extracts all data rows and columns from the database which is not needed as in most cases we need specific data fields depending upon some conditions like select names of the students belonging to a specific country or region.
So for this, we can use two Django query set methods defer() to specify which fields are not required and only() to determine which fields are only needed. In the case of a large number of fields and data, these methods are very useful because only those fields will be loaded which are required. And some fields can be restricted from loading if they are not required.
Let’s consider an example of a database having fields: id, name, age, contact, and address.
If we want to load only the names of the employees and their contacts then we can use the only() method as
Entry.objects.only(“name”,”contact”)
If we want to load information other than age and address then simply we can use the defer() method as,
Entry.objects.defer(“age”, “address”)
Furthermore, database indexing can also be used for the fast retrieval of data.
Code Optimization
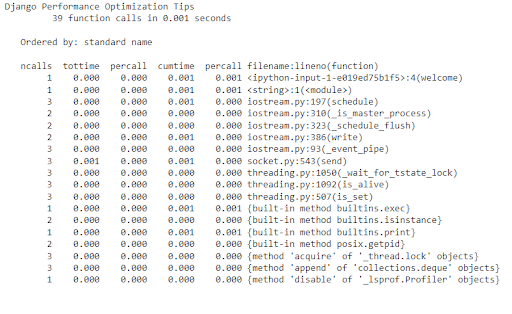
Code optimization is another important tip in which we can optimize some portions of the code depending upon the performance of that method by using python profilers such as cProfile or line profiler.
It depicts every method and the time taken for its execution separately. These insights help to optimize the code. Moreover, we can also go into a specific method and optimize it. Here is a demo code of cProfile profiler.
- import cProfile
- def welcome():
print(“Django Performance Optimization Tips”)
- cProfile.run(‘welcome()’)
In Django, we can use the Django rest framework which helps to create a complete API in just a few (two or maybe three) lines of code. Django rest framework testing helps to check what our program is doing and what response is it giving against the request and what we want it to perform. You can check our complete tutorial regarding the Django rest framework: Click here.
The time and space complexity of the code should also be considered for the optimization of code depending upon your need. Some external libraries can also be used for performance testing which includes line_profiler, memory_profiler, etc.
Caching
Caching is one of the most powerful and useful techniques which works as a booster for the retrieval of data. Django provides caching at different levels or for different parts of the site.
Consider that some parts of your code have heavy calculations which will be performed at every request. By using Django caching we can store these calculations on the cache so that there will be no need to do these calculations again and again as the results can just be fetched from the memory. We can cache our whole site by adding just 3 lines of code in the MIDDLEWARE list in the settings.py file which are:
'django.middleware.cache.UpdateCacheMiddleware', 'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware', 'django.middleware.cache.FetchFromCacheMiddleware'
Now let’s have a look at response time without caching:
We can see that It will speed up the whole process of responding to a request. Similarly, we can also save the resent responses in the cache as the user can send the same request again so in this case the response will be fetched more fastly than the response time of the first-time request.
In the Django cache framework, cache data can be stored in the database, in a file, or in memory.
Concept of Laziness
Laziness is to avoid anything to be performed. But Django uses it as a strategy as the parts which are lazy will avoid loading or execution until they are not required. So, these parts will load only when they are needed. It will save a lot of time.
Consider we have created a site having eight pages, out of which three are in lazy mode. In general, when we start loading the site without laziness, it will completely load the site (all eight pages) and then show any response, which will take a lot of time, but on the other hand, in case of laziness, only 5 pages will be loaded. The lazy three pages will only be loaded when we call them, depending upon the request or requirement.
Django provides the utility function keep_lazy(), which takes the first parameter as a string. It keeps the functionality to be performed on this string until it is not called or required. Let us take an example of QuerySets (query sets are lazy) for understanding the concept of laziness:
qSet = Entry.objects.filter(headline__startswith="Django") qSet = qSet.filter(pub_date__lte=datetime.date.today()) qSet = qSet.exclude(body_text__icontains="Performance") print(qSet)
Here the first three lines are creating three query sets and it seems that we are hitting the database three times but it is not the case. These lines are like simple instructions which will be executed only when needed like the database will be used only once when we call print(qSet).
Using Performance Booster Functions
Two primary methods can be used as boosters for Django performance optimization known as select_related() and prefetch_related(). Both of these functions make the program faster by reducing the number of queries.
The select_related() method is like an inner join, which can be written in both Python and SQL. But in the case of larger tables joining ts can’t perform well so in that case prefetch_related() method will be used which is although less effective and slower than select_related(). As it queries both tables and connects them using Python only but it is used for larger tables and many to many relations.
Latest Software Version
It’s good to have the newest versions of the software you are using. Although, it is not assured that the new version is always more effective, efficient, optimal, and secure.
But there is the possibility that new useful features, libraries, or tools are added that can provide optimality which is our main focus right now.
Managing a Large Number of Requests
It is common to have massive traffic or several requests on your site. Thus, it is also essential to manage them by using a performance booster. For example, you can add a Load Balancer or data compression tool that works as a tremendous potential performance accelerator.
Looking For a Django Development Team?
Share the details of your request and we will provide you with a full-cycle team under one roof.
How do Esketchers Help in Optimizing Your App?
Esketchers is a leading python application development and software consultancy company on Upwork and Clutch with a 99% success rate in project delivery. Our expert software engineers and solution architects have exceptional problem-solving abilities.
That’s why we’re among the top 1% of software houses in the United States. Looking for an exceptional Django app with 100% uptime and 99% response rate. Contact us or drop us an email: ✉️Info@leathersketch.com
The Final Verdict
Application optimization is an essential aspect of programming that can’t be ignored. So for the optimization of Django performance, some useful tips and techniques are mentioned and explained above. Every technique is different and has its level of optimization so you can use any of the above tips depending upon your requirement for optimization after evaluation and comparison.